The different versions and configurations of Power BI can be confusing. In this blog, we are comparing Power BI Desktop to Power BI Service. This will shed light on how to use each of these apps.

Power BI Desktop
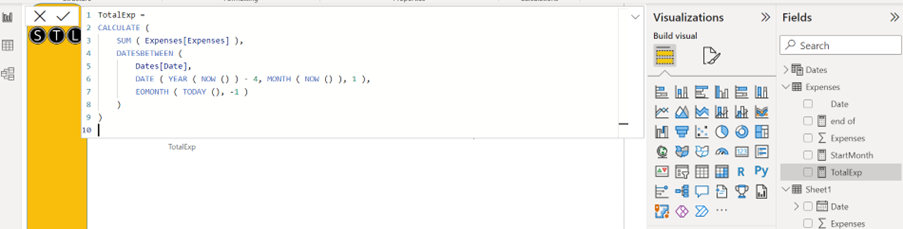
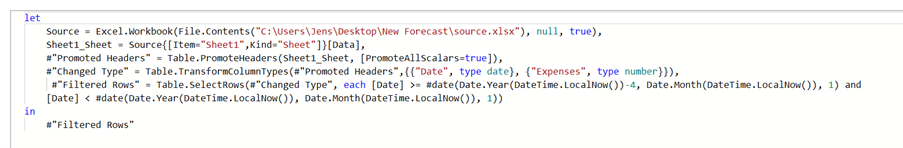
Power BI Desktop is a free application you can download and install on your local PC. You can use Power BI Desktop to connect to, transform, and visualize your data. Furthermore, you can analyse your data and develop reports. The Query Editor in Power BI Desktop manages the connections to the data sources. It can structure, clean, merge, and append data. You are then able to combine the data into a relational data model. From the data model, you can design reports using the visualisation tools in Power BI Desktop. Power BI Desktop is the only app of the two which allows the creation of DAX (Data analysis eXpressions) measures, calculations, and column calculations. You can set up role level security (RLS). You can use RLS to manage the data each person in the audience has access to in a published report.
the Power BI Service
The Power BI Service is known as Software as a Service (SaaS), which is a cloud-based service. You can edit reports, share the reports with your audience, and collaborate with teams and organizations. You can connect to certain data sources, but its modelling capability is limited. The Power BI Service cannot perform DAX measures, calculations, or column calculations. However, you can create dashboards from multiple reports using Power BI service. Furthermore, it is possible to create and distribute apps, reveal business insights, and much more.
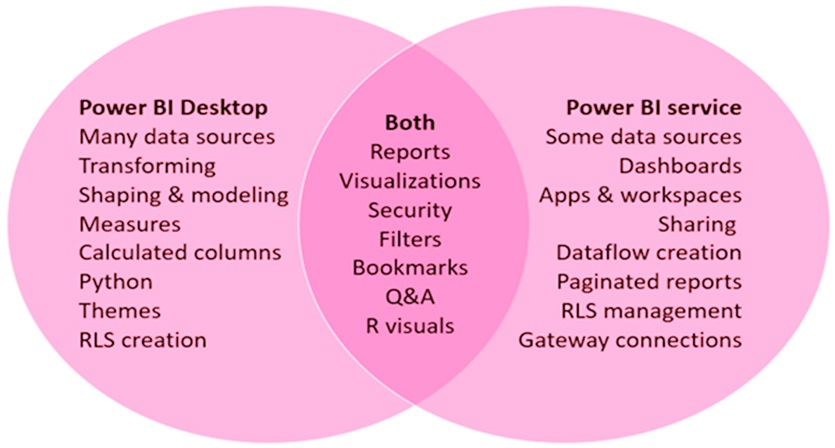
Power BI Desktop versus the Power BI service – diagram
The diagram above compares Power BI Desktop and the Power BI Service. As you can see, there are features common to both tools. However, certain tasks are unique to one app. The diagram also shows which features are only available in either Power BI Desktop or in Power BI Service.
Best practice is to do all the development work in Power BI Desktop, because of all the limitations you have in Power BI Service. The Query Editor is not available in Power BI Service. This means that you cannot shape, clean, merge, append, or group the data. Neither can you create data models, measures or column calculations.
Keep your activities strictly separated when using both apps. Do all development, updates, and changes to reports in Power BI Desktop. Save these changes in locally stored Power BI files. After the changes, simply publish the reports again. This will overwrite the old reports on Power BI Service. You can change the reports in Power BI Service and add more visuals, but this will not update your locally stored Power BI files.
Editing Power BI Reports
In both Power BI Desktop and Power BI Service, you can build and edit Power BI reports. A report can have one or more pages, with visuals and collections of visuals. You can also add bookmarks, buttons, filters, and drill-throughs to improve navigation in your reports.
Working in the Power BI service – Collaborating
Having created your datasets and reports, you can save them to workspaces in the Power BI Service, where you and your colleagues can collaborate. You can build dashboards on top of those reports. This enables you to share the dashboards and reports with consumers inside and outside your organization. In the Power BI Service, users can view reports in Reading view only, not in Editing view. Users do not have access to all the features accessible to report designers. You can, however, share your datasets and let others build their own reports from them.
Self-service data preparation with dataflows
Dataflows help organizations unify data from different data sources and organise it for modelling. Analysts can easily create dataflows, using self-service tools. They can also use dataflows to consume, convert, combine, and improve large data sets by defining data source connections, ETL logic, refreshing schedules, and more.
Conclusion
In summary, when comparing Power BI Desktop to Power BI Service, best practice is to use Power BI desktop for developing reports and Power BI Service to publish, share, and collaborate with others.
STL has four Power BI courses. All four courses are based on developing in Power BI Desktop. On our Power BI Reporting and Power BI Modelling, Visualisation and Publishing courses, we include Power BI Service in the course.